5 things to know about the Hungarian Language Exam
Thinking about taking the language exam to get official proof of your knowledge of Hungarian?
Great! 🙂
1. A monolingual exam
The entire exam (both oral and written) is conducted in Hungarian, without a mediating language (i.e. English). Therefore mediation skills, i.e. translation between Hungarian and another language and interpretation, are NOT measured. Sigh 🙂
2. Aligned to international guidelines
The Hungarian Language Proficiency Exam doesn’t just stand on its own: it follows and is based on the guiding principles of the European Council, called the Common European Framework Language of Reference for Languages (CEFR). The 6 reference levels of this guideline are the European standard for grading an individual’s language proficiency: A1, A2, B1, B2, C1 and C2. The good thing about this is that your certificate will be understood and accepted worldwide.
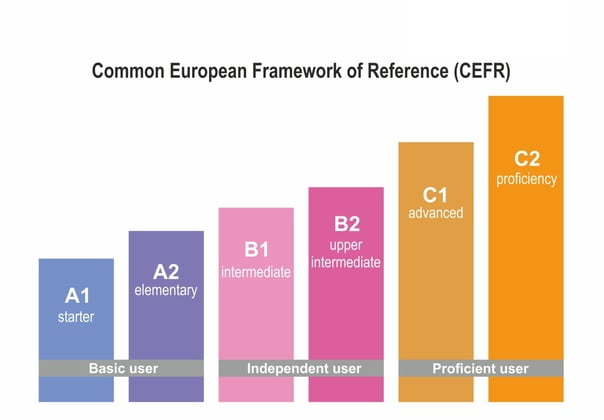
3. Three levels to choose from
You can take the exam at 3 accredited levels:
B1 – Alapfok (Intermediate)
B2 – Középfok (Upper Intermediate)
C1 – Felsőfok (Advanced)
You can also take the exam at A2 (Elementary) level but that would not be accredited. It could serve as an opportunity to make your feet wet and therefore prepare you for future, more advanced tests.
4. Skills measured
You will be tested at four areas: reading, writing, listening and speaking – just like any other language exam. Unless you choose to take only the written or the oral test (only possible at the Origó test, more about this below.)
5. Two types of exam to choose from
Currently two language exam systems offer Hungarian as a Second Language Exams: Origó and ECL (European Consortium for the Certificate of Attainment in Modern Languages).
When taking the Hungarian language exam, you have to choose one of the two. Read more about this.

